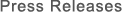Sharp Corporation (hereinafter "Sharp") will exhibit at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) booth at the 76th International Astronautical Congress (IAC 2025), which will be held from September 29 (Mon) to October 3 (Fri) at the International Convention Centre Sydney in Australia. The booth highlights three types of the latest space-qualified thin-film compound solar cells.
Left: Image of Sharp's space solar technology
Right: Booth Image (Exhibition Location: International Convention Centre Sydney, Stand: 154, Booth 'M-8')
The International Astronautical Congress (IAC) began in 1950. It is held to share the latest research results and technological innovations in the space industry and space science, attracting numerous participants from global space-related organizations, companies, and educational institutions. Since receiving component certification for space-qualified silicon solar cells from JAXA in 1972, Sharp has supplied space solar cells for over 50 years. At this congress, Sharp will showcase three types of the latest thin-film compound solar cells and provide proposals tailored to various applications in space.
■ Exhibit Highlights
Sharp will showcase three types of thin-film compound solar cells.
1. Film sheet type
This sheet structure encapsulates the solar cell with a thin film, providing lightweight and flexible features that enable mounting on curved surfaces. It was installed on Smart Lander for Investigating Moon 'SLIM', which successfully achieved high-precision landing on the lunar surface in January 2024. Even after the lunar landing, it continues to supply power necessary for communication with Earth for several months, demonstrating reliable performance in harsh environments.
2. Glass sheet type
This sheet structure uses a special glass for surface protection, which also exhibits excellent radiation resistance. It is highly efficient, lightweight, and possesses superior flexibility, making it suitable for long-term missions such as planetary exploration and deep space exploration. It is scheduled to be installed on Demonstration and Experiment of Space Technology for INterplanetary voYage with Phaethon fLyby and dUst Science 'DESTINY+', which JAXA aims to launch in FY2028.
3. Glass-encapsulated cell type
This is a CIC (Coverglass Integrated Cell) structure type, where cover glass is bonded to each cell. Until now, the adoption of CIC structures in thin-film compound solar cells has been challenging due to their thinness, but this has been made possible by Sharp's unique internal wiring technology. In addition to being highly efficient and lightweight, its stable operational performance in satellite panels has been recognized, leading to its selection for JAXA's Martian Moons eXploration 'MMX' (scheduled for launch in FY2026). Sharp will showcase a model with the same structure as the thin-film compound solar cells planned for 'MMX'.


 Choose
Choose