Resource Recycling
Approach to Resource Recycling
Towards the Realization of a Circular Economy
Sharp has provided the world with diverse value through the new products it creates but, at the same time, has consumed a large amount of resources. By making greater efforts to use resources more effectively and to provide maximum value with minimal resources, Sharp aims to foster a circular economy that will result in the realization of a recycling-based society. Specifically, Sharp focuses on the three areas of products, manufacturing, and recycling to create environmentally friendly products and devices, develop environmentally beneficial technologies, reduce the environmental impact of its business activities, recycle used products, and pursue other efforts across a wide range of domains.
Three-Area Approach
(1) Products: Sharp performs environmentally conscious design and life cycle assessments for newly developed products and strives to reduce virgin plastics and waste by conserving resources, extending product life, and using recycled materials. Sharp has also put into practical use a closed-loop material recycling technology that reuses plastics collected from used home appliances as components for new home appliances.
Keywords: Virgin plastics / Closed-loop material recycling technology
(2) Manufacturing: Sharp aims to reduce the environmental impact of its factories through the efficient use of resources. Sharp is working to reduce and recycle waste generated in the manufacturing process, while also actively reducing water withdrawal and recycling wastewater from processes in order to make effective use of water resources.
Keywords: Waste / Water resources
(3) Recycling: In addition to collecting and recycling used products, Sharp provides employees with design-for-recycling training and tours of recycling factories.
Keywords: Recycling used products / Design-for-recycling training
Resource Recycling Focus Areas

Reducing Virgin Plastics
Approach to Reducing Virgin Plastics
Due to their usefulness, plastics are used in a wide range of products, containers, and packaging, making them essential materials in modern society. At the same time, however, the recycling of plastics is becoming increasingly important both domestically and internationally, prompted by issues such as ocean plastic pollution and the depletion of oil resources.
Sharp has set a medium-term target for virgin plastics in order to strengthen its efforts to reduce the amount of virgin plastics used in its products and packaging. To achieve this target, Sharp has established a subcommittee and is working to use more plastic alternatives, recycled plastics, and bioplastics.
Medium-Term Target for Virgin Plastics
To ensure its efforts aimed at resource recycling, Sharp has joined the Circular Partners*1 and has set the following target as it works to help realize a circular economy.

| Target indicator | Percentage of products using recycled plastics or bioplastics among new products for the reporting year |
|---|---|
| Target level | 70% or more |
| Target year | Fiscal 2030 |
Virgin Plastic Reduction Subcommittee
In order to steadily advance its efforts to reduce the amount of virgin plastics used, Sharp has established a Virgin Plastic Reduction Subcommittee comprised of in-house engineers. This subcommittee holds discussions on virgin plastic reduction and shares relevant information and trends.
Examples of Virgin Plastic Reduction
In order to reduce the amount of virgin plastics used, Sharp is actively working to switch to plastic alternatives and to adopt recycled plastics and bioplastics.
| Packaging and products | Using recycled plastics and less plastic The MFP main body is made of approximately 50% recycled plastic, and packaging materials like corrugated cardboard and other eco-friendly materials are used in place of polystyrene foam, significantly reducing the amount of plastic waste. 
 |
|---|---|
| Products |
Example of recycled plastic use
Smartphone casing is made of approximately 60% recycled plastic. 
|
|
Example of bioplastic use
The egg tray included with Plasmacluster refrigerators*2 uses a biomass composite plastic containing bamboo powder, which has antibacterial properties*3. 
|
- A Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (Japan)-led partnership between industry, government, and academia, which is focused on the circular economy.
- Fit63 series: SJ-MF55P/MF51P/MF46P/MF43P/MW46P
- Tester: Kaken Test Center General Incorporated Foundation; Test method: JIS Z 2801 antibacterial test; Antibacterial method: 2,6-dimethoxy-1,4-benzoquinone and tannin; Test subject: Egg tray; Test result: Antibacterial effect of over 99%
Environmental Technologies That Contribute to a Sustainable, Recycling-Based Society
| Fiscal 2024 Objectives | Fiscal 2024 Achievements | Self-Evaluation | Priority Objectives for Fiscal 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
★★★ |
|
- Self-evaluation: ★★★ Achieved more than targeted / ★★ Achieved as targeted / ★ Achieved to some extent
Expanding the Use of Recycled Plastics
In recycling materials, such as when end-of-life plastic is reused to make new products, the open-loop material recycling scheme is commonly adopted. It involves reusing recycled materials to make things like daily necessities and sundries. The majority of these are used only once and disposed of as municipal waste.
As opposed to this type of recycling, Sharp and Kansai Recycling Systems Co., Ltd.*1 jointly developed closed-loop plastic material recycling technology with a view to making better use of finite resources and reducing waste. This technology enables the repeated recovery of plastic from used consumer electronics products as well as the reuse of that plastic in parts of new consumer electronics products. The technology has been in practical use since fiscal 2001, when the Act on Recycling of Specified Kinds of Home Appliances (Home Appliance Recycling Act) was enacted in Japan.
Sharp has been striving to make more plastic recyclable through the development of new technologies. These include a technology for recovering high-purity polypropylene (PP) from mixed plastic parts and parts that contain metal; a technology for improving the properties of recovered PP, HIPS*2, and PC+ABS*3 materials so that their quality is on a par with that of virgin materials; a technology that gives materials added value by imparting properties such as flame retardancy, weather resistance, and an antibacterial property, with the aim of expanding applications for recycled plastic; and a quality-control technology for ensuring optimal quality. Thanks to the development and introduction of these technologies that integrate everything from recovery to quality control, Sharp has been able to establish closed-loop material recycling to produce high-grade recycled plastic.
- A consumer electronics recycling company established in Japan with joint investment from Sharp, Mitsubishi Materials Corporation, and four other companies.
- High-impact polystyrene (general-purpose polystyrene [GPPS] given impact resistance by adding rubber).
- A polymer alloy of polycarbonate and acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene (a resin given new properties as a result of mixing in several types of polymers).
Recycling Plastic Recovered from the 4 Types of Home Appliances

- Blending multiple types of resins uniformly and finely dispersed into one another at the molecular level.
- A resin given new properties as a result of mixing in several types of resins.
Expanding the Use of Recycled Plastics
Sharp is pursuing greater recycling of used plastics, not only through horizontal recycling, in which used plastics are made as good as new material and incorporated into the same parts as they were originally used, but also through upgrade recycling, in which the recycled plastic is given added value with flame retardancy, weather resistance, high stiffness, or color.
In fiscal 2024, Sharp developed white recycled polypropylene using polypropylene recovered from used refrigerators as the raw material. This provides a significant improvement in appearance, which was a challenge for recycled plastics, while maintaining the physical properties and durability required for home appliances. Sharp has adopted this material for use in the exterior parts of its refrigerators. Traditionally, recycled plastics have been limited to use in internal parts due to appearance issues, such as black spots caused by impurities, like environmental dirt and foreign matter, and uneven coloring caused by variations in raw materials. Now, thanks to technology jointly developed with Kansai Recycling Systems, the entire process from separation, collection, and sorting of the raw materials to recycling has been optimized. By using Sharp’s proprietary recycling technology, it has become possible to mass-produce high-quality white recycled plastic that can be used in the exterior parts of home appliances. This technology makes it possible to expand the scope of application of recycled plastic and is, therefore, expected to further increase the rate of recycled plastics used in products.
Additionally, as a new initiative, Sharp is pursuing the development of recycled high-impact polystyrene (HIPS) made from polystyrene recovered from used home appliances. Polystyrene is one of the main types of plastic used in home appliances, but, because it is susceptible to thermal degradation and the adverse effects of foreign matter, it is difficult to utilize in horizontal recycling via conventional technology. Thus, until now, it has been used for things like everyday items and miscellaneous goods. In fiscal 2024, Sharp completed the basic development of technology needed to separate and recover polystyrene, as well as development of formulation technology to improve the physical properties of polystyrene to the same level as new material. Moving forward, Sharp will work to steadily advance development of durability and mass production technologies, with a goal of achieving practical application by fiscal 2025.
Used Plastic Recycling Method

Examples of Colored Recycled Polypropylene Use

Establishing a Circular Economy
The use of recycled plastics developed through Sharp’s own closed-loop material recycling technology was extended to refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, and small appliances released in fiscal 2024. In fiscal 2024, the cumulative total amount used since fiscal 2001 reached 21,000 tons.
In fiscal 2024, Sharp began using recycled PC+ABS from flat-panel TVs for parts in MFPs that require environmental labels*. Sharp will expand this plastic recycling technology, which began with four types of home appliances, to a wider range of other Sharp products in an effort to reduce the environmental impact of its products.
Moving forward, Sharp aims to expand closed-loop material recycling to all of its products, not just these four home appliances, to contribute to the realization of a circular economy.
- Labels are given to products and services to certify that they help reduce the environmental impact on the Earth. EPEAT, Blue Angel, Eco Mark, others.
Establishing a Circular Economy

Examples of Recycled Plastic Use









| Product | Part | Recycled Plastic | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Washing machine | Washing tub | PP | Washing machine tub |
| Refrigerator | Duct cover, pump cover | Refrigerator vegetable case | |
| Shower duct cover, refrigerator divider, other | |||
| Evaporator cover | Washing machine spin tub, balancer, other | ||
| Air conditioner | Condensation cover, motor holder | ||
| Stick vacuum cleaner | Stand, nozzle, other | Air conditioner, refrigerator, and washing machine parts | |
| Ceramic fan heater | Casing | Flame-retardant PP | |
| Air purifier | Power supply box | Flame-retardant HIPS | Flat-panel TV back cabinet |
| Car Plasmacluster Ion generator | Internal parts | Flame-retardant PC+ABS | Flat-panel TV back cabinet |
| MFP | LCD holder, other | ||
| Handheld device (Handy Terminal) charger | Charger |
Expanding the Recycling of Used Products
| Fiscal 2024 Objectives | Fiscal 2024 Achievements | Self-Evaluation | Priority Objectives for Fiscal 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
★★ |
|
- Self-evaluation: ★★★ Achieved more than targeted / ★★ Achieved as targeted / ★ Achieved to some extent
Sharp’s Stance on Recycling Used Products
Sharp collects and recycles used products in compliance with the recycling laws and regulations of the respective country or region. Through the effective use of limited resources, Sharp is, in cooperation with consumers and recyclers, contributing to the realization of a sustainable society.
Japan: Recycling 4 Kinds of Home Appliances in Japan (Air Conditioners, TVs, Refrigerators, and Washing Machines)
As a member of the B Group*1 for home appliance recycling, Sharp has constructed—and is operating—a highly efficient recycling system consisting of 19 recycling plants in Japan. In fiscal 2024, Sharp collected 2.297 million units (up 1% over the previous fiscal year) of the four types of appliances covered by the Home Appliance Recycling Act. The processed and recycled weight amounted to approximately 64,000 tons (down 1% over the previous fiscal year). For all four appliance types, Sharp’s rate of recycling exceeded the legally stipulated levels.
- The B Group consists of Sharp Corporation, Sony Corporation, Hitachi Global Life Solutions, Inc., Fujitsu General Ltd., Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, and other companies.
Sharp Corporation’s Recycling Results for 4 Home Appliance Types (Fiscal 2024)
Note: All figures are rounded down to the nearest whole number.
| Unit | Air Conditioners | CRT TVs | Flat-Panel TVs | Refrigerators/ Freezers | Washing Machines/Dryers | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units collected from designated collection sites | 1,000 units | 360 | 62 | 985 | 442 | 442 | 2,297 |
| Processed and recycled units | 1,000 units | 351 | 63 | 989 | 439 | 439 | 2,286 |
| Processed and recycled weight | Tons | 14,219 | 1,349 | 14,934 | 25,548 | 17,933 | 73,986 |
| Recycled weight | Tons | 13,540 | 1,002 | 12,944 | 20,551 | 16,937 | 64,976 |
| Recycling rate | % | 95 | 74 | 86 | 80 | 94 | - |
| Legally required recycling rate | % | 80 | 55 | 74 | 70 | 82 | - |
Toward Making Better Use of Resources
Sharp and Kansai Recycling Systems Co., Ltd.*2 have joined forces to make effective use of resources and to improve recycling efficiency.
In the recycling process, the unloading of containerized washing machines has, up until now, been done manually, but as front-loading washing machines weigh between 60 kg and 80 kg, this was physically demanding for the workers. Therefore, in fiscal 2023, Sharp introduced a tilting device that automatically loads washing machines into the supply work area, and, in fiscal 2024, it introduced a transport conveyor to improve work efficiency and safety. As a result, conveyance efficiency has improved by 29% and work efficiency has improved by 3%.
- A consumer electronics recycling company established in Japan with joint investment from Sharp, Mitsubishi Materials Corporation, and four other companies


Recycling Used Products and Communicating with Local Communities
In accordance with the Home Appliance Recycling Act, Kansai Recycling Systems Co., Ltd. recycles four types of used home appliances (air conditioners, TVs, refrigerators, washing machines) in Hirakata, Osaka Prefecture and Iga, Mie Prefecture. Kansai Recycling Systems publicizes its activities by collaborating with the local government and board of education to, for example, give factory tours to elementary and junior high students and lead classes at their schools. As well, the company recently took part for the first time in a careers event*1 for junior and senior high school students. In fiscal 2024 the company welcomed a total of 1,695 visitors from Japan and overseas, bringing the cumulative visitor total to more than 33,000 people. Kansai Recycling Systems also continued to participate in off-site lectures and local events*2. These included a washing machine dismantling demonstration and a participatory washing machine lid dismantling.

Left: Demonstration of dismantling a washing machine
Right: Young participants dismantle a washing machine lid
- School lessons in which people working in various jobs are invited to lead the class and talk about their work, showing students how interesting work can be and widening their opportunities for the future.
- At Hirakata Eco Forum 2024 (February 10, 2024), the company demonstrated how a washing machine is dismantled; at Holantotte Hirakata Resource Recycling Symposium (March 9, 2025), participants could try dismantling a washing machine lid.
Design-for-Recycling Training
Sharp is committed to considering the whole life cycle of products it manufactures. Together with Kansai Recycling Systems—where four kinds of Sharp products are recycled—Sharp has been holding design-for-recycling training for product planners and designers. In November 2024, eight people including those in charge of TVs took part, and in April 2025, 25 people in charge of white goods took part in the training.
The training emphasized the importance of designing products with an eye to their eventual recycling, with a focus on plastic material recycling. It also included a tour of the recycling plant. Participants practiced dismantling products, including a fully automatic washing machine in use for over a decade, an air conditioner with automatic filter cleaning, a refrigerator, and an OLED TV, which came under the Home Appliance Recycling Act in fiscal 2024. They saw how the ease of dismantling depends on the fastening method used—for example, whether the product is held together with screws—and learned the importance of separating components into discrete material types. They also learned about material labeling and design considerations in ensuring high-quality recycling and listened to feedback from the workers.
Participants gained a better understanding of the recycling process, and expressed a desire to focus on achieving both quality and recyclability in their future designs. We will continue to foster awareness within the company so that we can pursue manufacturing that considers everything from material selection to end-of-life recycling.


Reusing and Recycling Copiers and MFPs in Japan
Sharp is reusing and recycling copiers and MFPs collected both through Sharp distribution channels and through common industry channels. The company is also collecting used toner cartridges and remanufacturing them to the same quality standard of new products, thus assuring that customers will always get the same high quality. Sharp designs its toner cartridges for easy reuse and recycling. This ensures durability and reduces the amount of time needed to reprocess used cartridges.
North America
In 2007, Sharp’s American manufacturing and sales base SEC established MRM (Electronic Manufacturers Recycling Management Company, LLC)*1 to manage recycling of AV products. Growing nationwide efforts have seen a total of 2,050 collection points established for used products. MRM operates in accordance with the laws and regulations of each state and recycled a total of 62,000 tons of used products in fiscal 2024.
In addition, since 2008, as part of its efforts to protect the environment and reduce landfill waste, SEC has been working with recycling companies to recycle all Sharp consumables, including toner cartridges, bottles, toner collection containers, and drum units. SEC encourages recycling by covering the materials and costs required to return used products.
- MRM is a joint venture with Panasonic Corporation of North America and Toshiba America Consumer Electronics, LLC.
Canada
With the cooperation of its recycling partner, EPRA (Electronic Products Recycling Association), Sharp’s Canadian sales base SECL recycled more than 201,405 kg of Sharp products in Ontario in 2024. This includes electronics across all product sectors, including printers, displays, and consumer products.
SECL and EPRA are committed to complying with Ontario regulations, which require more products to be recycled each year. SECL’s goal for 2025 is to recycle 236,997 kg of electronic devices, and the company has concluded an agreement with EPRA to achieve this goal.
Sweden
Sharp’s sales base in Sweden, SBS-SE, has launched a new partnership program called the Circular Ambassador Program in collaboration with Inrego AB to promote circular business as an ambassador while also expanding partnerships with other businesses in the Nordic region.
SBS-SE achieved 26,501 kg CO2e*2 in recycled products and received a certificate from Inrego. This is equivalent to the energy needed to run 2,544 refrigerators for a year, to heat 106 apartments for a year, or to drive around the world four times.
- CO2e: CO2 equivalent

Australia
Sharp’s Australian sales base SCA is a member of the APCO (Australian Packaging Covenant Organisation) and is a signatory to the Australian Packaging Covenant. Members agree to shared responsibility and joint efforts. SCA works with government and industry to achieve sustainable packaging through material reduction, design, specific recycling rates, landfill waste reduction, alternative materials, and circular economy activities.
SCA also uses Ecycle Solutions to collect e-waste and expanded polystyrene from its work sites and warehouses. Ecycle Solutions is approved and monitored by the local government to ensure minimization of waste to landfills by recycling in the correct manner. In addition, SCA is introducing similar systems at its partner locations.
Minimizing and Recycling Business Activity-Linked Waste
| Fiscal 2024 Objectives | Fiscal 2024 Achievements | Self-Evaluation | Priority Objectives for Fiscal 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
★★ |
|
- Self-evaluation: ★★★ Achieved more than targeted / ★★ Achieved as targeted / ★ Achieved to some extent
Curbing the Amount of Waste, etc. Generated
Sharp has been working to reduce waste and to recycle as much of it as possible in an effort to contribute to building a circular economy.
In fiscal 2024, the amount of waste, etc. generated by Sharp decreased by 21% compared to the previous fiscal year to 75,000 tons. The amount of recycling was 57,000 tons. Meanwhile, the final landfill disposal rate was 0.33%—low enough to achieve our third year in a row of zero discharge to landfill*1 on a global scale.
Sharp will continue to strengthen waste-reduction efforts at overseas bases while maintaining global zero discharge to landfill.
Appropriate Storage and Management of PCB Wastes
In Japan, Sharp properly stores and manages waste PCB (polychlorinated biphenyls) in accordance with the Act on Special Measures Concerning Promotion of Proper Treatment of PCB Wastes. Sharp has completed processing of all high-concentration waste PCB in fiscal 2022. As for the remaining low-concentration waste PCB, Sharp is on track to finish processing them at the earliest date possible.
- Sharp defines “zero discharge to landfill” as a final landfill disposal rate of less than 0.5%. Final landfill disposal rate (%) = Amount of landfill disposal ÷ amount of waste, etc. generated × 100.
- Of general waste and industrial waste, waste that contains no hazardous substances.
- Waste designated as ‘specially controlled industrial waste’ in Japan and as ‘hazardous’ in countries/regions around the world.
Amount of Waste, etc.

Amount of Recycling

Waste, etc. by Region (Fiscal 2024)

Final Landfill Disposal Rate

Reducing Industrial Waste through Cleaning of Waste Liquid Concentrators
At the Kameyama Plant (Kameyama, Mie Prefecture), we strive to reduce the amount of industrial waste generated in the LCD production process.
The cleaning liquid (sodium fluoride) used to clean the toxic gases generated in the production of LCDs is reduced in volume in evaporator concentrators before being disposed of as industrial waste. The processing ability of the evaporator concentrator, however, decreases when it evaporates the waste liquid and crystals are generated.
In fiscal 2024, we began periodically cleaning the evaporator concentrators with high-pressure water to lessen the deterioration of their processing ability. This helped achieve an annual decrease of 1,320 tons.
Flow of Cleaning Waste Liquid Treatment Process

Effectively Using Water Resources
| Fiscal 2024 Objectives | Fiscal 2024 Achievements | Self-Evaluation | Priority Objectives for Fiscal 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
★ |
|
- Self-evaluation: ★★★ Achieved more than targeted / ★★ Achieved as targeted / ★ Achieved to some extent
Sharp’s Stance on Water Resources
Water resource problems are arising on a worldwide scale with the increase in the world’s population, the economic growth of developing countries, climate change, and other factors. Sharp is striving to make effective use of water resources in line with the environmental conservation guidelines stipulated in Sharp’s Basic Environmental Philosophy, the Sharp Group Charter of Corporate Behavior, and the Sharp Code of Conduct. In particular, Sharp recognizes that securing the water resources necessary for the production of LCDs and other electronic devices is a serious issue that could affect business continuity. That is why Sharp is pursuing the reduced use of new water and an increased use of recycled water.
Reducing the Amount of New Water Used and Using More Recycled Water
The volume of new water used by Sharp in fiscal 2024 decreased by 5% compared to the previous fiscal year to 8.8 million m3. The improvement rate of water intensity was 5%. To minimize the effects on business continuity of the risk of water shortages, Sharp assesses water risk at its plants using the Aqueduct assessment tool developed by the World Resources Institute (WRI). SATL, Sharp’s production base in Thailand, is located in an area of highest risk. It is therefore reducing its use of new water by recycling water discharged from the production process and other sources.
The Kameyama Plant (Kameyama, Mie Prefecture, Japan) and the Mie Plant (Taki District, Mie Prefecture, Japan) require a large amount of water in the production process for LCDs and other products. All of the water discharged from the production process is collected and reused via a closed-loop recycling system adopted at both plants. Through measures such as this, Sharp is maintaining a recycling rate* of at least 60%. Looking ahead, Sharp will pursue further water-use efficiency worldwide and boost production efficiency in accordance with business expansion.
In fiscal 2024, there were no litigation issues, fines, or penalties due to violations of water-related laws and regulations. There were also no serious water-related accidents.
- Recycling rate = Amount recycled ÷ (amount of new water + amount recycled).
Volume of New Water Used

New Water Used by Region (Fiscal 2024)

Water Recycling Rate

Water Used and Drainage by Region (Fiscal 2024)
(m3)
| Region | water withdrawal*1 | Effluent | Amount consumed*3 | Amount recycled | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Third-party water*2 | Groundwater | Total | surfase water | Sewerage | Seawater | Groundwater | Total | |||
| Japan | 6,224,211 | 537,391 | 6,761,602 | 3,379,046 | 308,744 | 1,456,881 | 0 | 5,144,671 | 1,616,931 | 17,391,150 |
| Asia | 776,679 | 10,401 | 787,080 | 31,454 | 415,808 | 0 | 0 | 447,262 | 339,818 | 211,484 |
| China | 1,216,448 | 0 | 1,216,448 | 0 | 981,229 | 0 | 0 | 981,229 | 235,219 | 176,987 |
| North and South America | 171 | 0 | 171 | 0 | 171 | 0 | 0 | 171 | 0 | 0 |
| Europe | 7,763 | 0 | 7,763 | 0 | 7,418 | 0 | 0 | 7,418 | 345 | 0 |
| Total | 8,225,272 | 547,792 | 8,773,064 | 3,410,500 | 1,713,370 | 1,456,881 | 0 | 6,580,751 | 2,192,313 | 17,779,621 |
Volume of New Water Used by Water Stress Rank*4(Fiscal 2024)
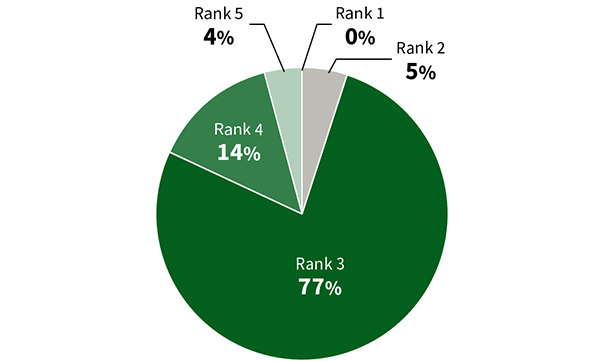
Volume of New Water Used in Water Stressed Regions*5(Fiscal 2024)
(m3)
| Region | Third-party water | Ground- water |
surfase water |
Seawater | Produced water |
Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | 34,685 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 34,685 |
| Asia | 729,517 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 729,517 |
| China | 835,645 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 835,645 |
| North and South America | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Europe | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 1,599,847 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1,599,847 |
- Surface water, seawater, and produced water was 0.
- Industrial-use water and tap water.
- Water consumption = Water withdrawal – Effluent.
- Under Aqueduct, each region is assigned a water stress score. There are five levels, from rank 1 (low risk) to rank 5 (high risk).
- Areas with an Aqueduct water stress score of rank 4 or higher.
Closed-Loop Water Recycling System
The Mie Plant (Taki District, Mie Prefecture) has adopted a closed-loop water recycling system to repeatedly recycle the large amount of water used for the production of displays. The water discharged from the production process contains chemicals that must not be released from the plant untreated. All of this water is collected and goes through steps such as passing through filters and biofiltration (the natural decomposition of chemicals using microorganisms), before being purified with dedicated equipment. The resulting water is used repeatedly in production.
Closed-Loop Water Recycling Flow

Digital Monitoring of Water Meters and Recycling of Washing Machine Wastewater
SSEC, Sharp’s production base in China, improved the efficiency of water resource use through digital monitoring of water meters and recycling of washing machine wastewater. For this, the company was honored as a Shanghai Water-Saving Demonstration Enterprise.
Water meters installed at SSEC connect to a digital monitoring platform. The meter sends water-use data in real time so that it can be confirmed on smartphones and PCs. This system monitors pipes in the entire plant 24-7 and enables immediate detection of water leaks. Furthermore, a proprietary SSEC washing water recycling system also contributes to the company’s water savings. In the plant, large volumes of wastewater are generated in trial operation of washing machines. This wastewater is stored, then used as cooling water for air conditioning and as water for flushing toilets.
Flow of Washing Machine Wastewater Recycling
